Function of the Upper Airway
Definition
The functions of the upper airway are heat and moisture exchange, thermoregulation, filtration and speech.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vocal cords open to allow breathing and close during swallowing to protect the lungs. |
|
|
- The efficiency of the nose to warm and humidify air is affected by the temperature and dryness of inhaled air.
- The nose is twice as effective as the mouth in humidifying air.
- Dryness will decrease the function of the cilia and decrease filtration.
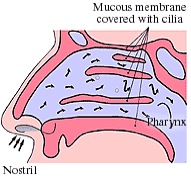 The nose heats air by changing blood flow of the nasal mucosa to warm to 32-34° C.
The nose heats air by changing blood flow of the nasal mucosa to warm to 32-34° C.
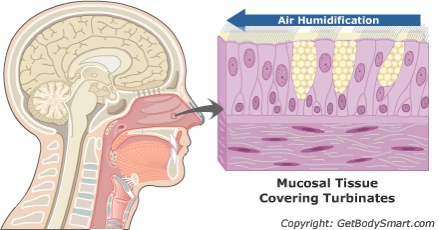 The nose humidifies air as it flows past nasal mucosa containing small glands that secrete fluids into the nasal cavity, and recovers moisture from exhaled air.
The nose humidifies air as it flows past nasal mucosa containing small glands that secrete fluids into the nasal cavity, and recovers moisture from exhaled air.
 The nose filters air by catching dust and other particles in the mucus. Cilia move the mucus to the pharynx where it is expectorated or swallowed.
The nose filters air by catching dust and other particles in the mucus. Cilia move the mucus to the pharynx where it is expectorated or swallowed.
 Voice is produced when the vocal cords close while exhaling air.
Voice is produced when the vocal cords close while exhaling air.